Other than direct sales by producers, there are two major ways to reach end consumers: retail stores and the hospitality industry.
In many markets, retail sales are much higher, accounting for about 80% of sales in the UK.
1. Retailers
1. Supermarkets

In many markets, Supermarkets have the largest share of wine sales. This makes it a very attractive option for producers who want to sell large quantities of wine.
| Advantages | ・Supermarkets can sell large quantities of wine. ・The ability to sell private label wine (Supermarkets’ own brand) can increase customer loyalty. ・Expertise in quality control, wine styles, etc., can be useful in other sales channels. ・For artisanal producers, this can be an opportunity to expand sales channels. |
| Disadvantages | ・Supermarkets have strong bargaining power, resulting in lower selling prices ・Additional promotional costs ・Strict quality control, shipping, and labeling requirements must be met ・Producers risk not being able to continue contracts if they do not meet Supermarkets’ sales expectations (risk of huge inventories) |
2. Deep Discounters

Deep Discounters are retail stores that function like supermarkets, but sell at lower prices. Their characteristic is that they sell products at permanently low prices, and they rarely have limited-time promotions.
- Profit from thin margins and high sales.
- Most products are private label.
- Tend to prefer to deal with minor producers with low overhead costs, including marketing costs (focus on production costs and quality).
| Advantages | ・Deep discounters often buy directly from producers to eliminate intermediate costs. ・Deep Discounters may be more profitable than wholesalers in supermarkets because they do not incur promotional costs. ・Can sell off excess wine inventory. ・Increasing share of sales (In the UK, wine drinkers’ share of buyers has increased from 23% in 2012 to 37% in 2018) |
| Disadvantages | ・Producers do not know if they can continue to do business with Deep Discounters. |
3. Convenience Retailers

Convenience retailers are becoming more and more important as they are more closely connected to people’s lives, operating “anytime” and “anywhere”.
| Advantages | ・Convenience Retailers have more sales opportunities ・Long business hours ・Close to people’s living areas ・Large chains may have their own brands, handling brands that are popular with local consumers. |
| Disadvantages | ・Selling price tends to be higher due to higher cost of store operation |
4. Specialist Wine Retailers

Specialist Wine Retailers are retailers that specialize in wine, with some specializing in wines and foods from specific countries. Some are large chains, but most are privately owned or small chains.
| Advantages | ・Consumers who buy at wine specialty stores spend more per bottle (opportunity to sell premium wines) ・High profit margins can be expected due to high prices. |
| Disadvantages | ・Specialist Wine Retailers have a small sales volume per store. As a result, they tend to outsource sales to agents, which tends to increase costs. ・Consumer service is costly (stores need to hire highly specialized staff and provide high quality customer service) |
Examples of customer service
- Tell the story of the wine to your customers
- Provide information on lesser-known regions and varieties
- Suggest food pairings
- Build relationships with regular customers to understand their likes and dislikes and then suggest new wines
- Let customers know when their favorite wines are on sale.
- Organize events such as tastings and wine classes
5. Hybrids

Hybrids are wine stores with bars and other facilities. Therefore, the store can serve food and drink wine.
| Advantages | Tasting wine can encourage consumers with little knowledge of wine to purchase wine. ・Reach out to a wider range of consumers. ・Introduce minor wine regions and varieties |
| Disadvantages | ・Longer business hours (need to stay open until late) ・Need to increase the number of customer service staff ・Additional facilities such as a kitchen are required. ・More government offices and procedures |
6. Online Retailing

In many countries, online sales are on a significant upward trend. However, its importance varies by country, accounting for 20% of sales in China but only 2% in the US.
| Advantages | ・Retailers can operate out of suburban warehouses, eliminating the need for costly retail stores. ・With lower costs, online retailers can carry more products. ・Can have a larger customer base than brick-and-mortar stores. |
| Disadvantages | ・Wine is heavy and bulky, so shipping costs tend to be high. ・There is a risk of loss or damage to the wine when it is transported. ・Consumers tend to demand shorter delivery times, and stores need to be able to meet these requirements. |
It is also necessary to build a website that is reliable and conveys the brand image.
- Creating an easy-to-use website
- Detailed descriptions of wines
- Suggestions for food and wine pairings
- Comments from staff and wine critics
- Information on medals won in wine competitions
- Keep content up to date (new wine arrivals, inventory updates)
7. Global Travel Retails
Global Travel Retails is a store set up at airports and other locations for travelers.
| Advantages | ・Consumers (tourists) have more time to look at products. ・Travelers tend to seek out high-priced products that are not available in their home country (opportunities for premium wine sales) |
| Disadvantages | ・Free trade agreements have reduced the importance of tax exemptions. ・High cost of retail space results in low profit margins |
8. Wine Investment Companies
Wine Investment Companies specializes in the procurement and sale of wine for investment.
Investment companies buy wines that fetch very high prices due to their rarity, either through producers or vendors, and sell them to customers. In effect, some companies act as brokers.
- London: Traditionally a center for wine investment, with many leading wine investment companies based in London.
- China: In 2008, the Hong Kong government abolished excise duties on wine in an effort to become the “hub of the East Asian wine trade,” and investment has intensified.
2. Hospitality Sector
The average price of wine sold in the hospitality industry is often higher than in retail stores. While the volume of wine sold in the hospitality industry is 20%, the value of wine sold in the hospitality industry is nearly 40%.
1. Bars

In terms of wine, it can be categorized into two types: wine-specific bars and general bars.
| Specialist Wine Bars | ・Similar to wine specialty retail stores ・Target consumers are people “high involvement” in wine Many stores focus on a specific country or style of wine. ・They tend not to offer famous brand wines, as they are not price competitive, they tend to carry wines from smaller producers |
| General Bars | ・Wine is just one of the beverages served. ・Wine is usually produced by large companies and is from well-known regions and varieties. ・Mostly inexpensive or moderately priced wines with a wide range of appeal. |
2. Restaurants

Restaurants can be classified according to the purpose of the meal itself, and the quality of the wine they serve depends on its importance.
| Non-Destination Restaurants | ・Restaurants that are not primarily for dining (e.g., between theaters, movies, after-work meals, etc.), often chain restaurants. ・General Bars as well, mostly inexpensive to moderately priced wines of well-known regions and grape varieties. |
| Casual Dining | ・Restaurants used for a wide range of occasions, from casual dining to long hours, many of which are privately owned or small chains ・Mostly medium to premium priced wines. ・In addition to wines from well-known regions and varietals, there is often a mix of lesser-known wines. ・Staff are trained to advise customers on wines based on their preferences, prices, and food pairings. |
| Fine Dining | ・Food is the destination, and the food and experience at the restaurant is the reason for the visit. ・Food and wine pairing is very important, and super premium wines are available in limited quantities. ・Being on the wine list is a source of great pride for producers. ・Wine is difficult to obtain, so it is generally purchased through an intermediary. |
3. Special Market Environments
In some countries, alcohol sales are strictly regulated, and in such countries, a special market has been formed.
Typical markets are the national monopoly market and the three-tier system in the US.
1. Monopoly Markets

In the Nordic countries and Canada, the government has a monopoly on the retail sale of alcoholic beverages.
- Sweden: Systembolaget, a government-owned chain, is the only retail outlet that can sell alcohol
- Ontario, Canada: fully controlled by the Liquor Control Board of Ontario (LCBO)
The purpose of monopoly sales is to limit the consumption of alcohol, which has the following systems and impacts.
- High taxes on alcoholic beverages, making them very expensive
- There is no incentive to advertise or lower prices.
- Wine purchasing is very complicated due to the bureaucratic system. However, since the final decision is based on quality alone, it may be adopted regardless of the size of the producer.
2. The USA’s Three-Tier System
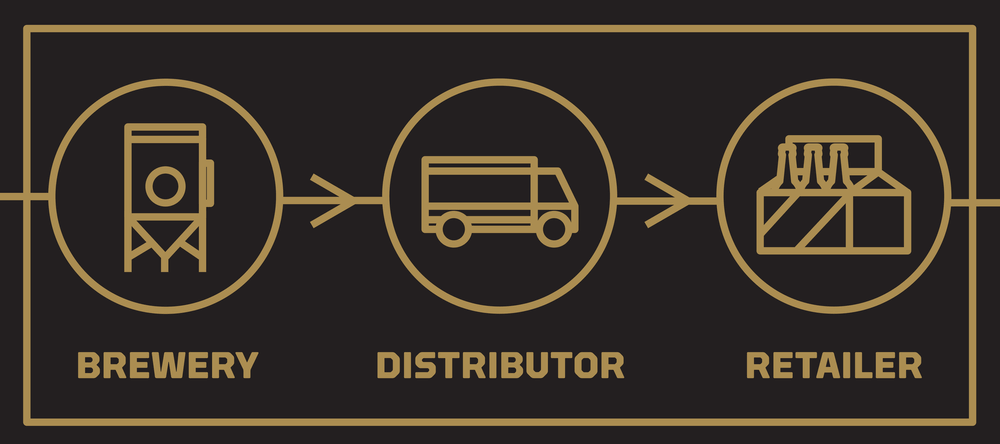
In the U.S., the distribution and sale of alcoholic beverages is governed by strict and complicated laws in each state. Therefore, doing business with alcohol in the US is not an easy task.
Vendors are grouped into three tiers, and cross-ownership between retail and other tiers is limited or completely prohibited.
- Suppliers: including producers and importers
- Distributors: including wholesalers and brokers
- Retailer: including retailers and HoReCa
This law is a remnant of Prohibition, which was repealed in 1933, and is designed to avoid a return to the pre-Prohibition era. (Gambling, known as saloons. Prostitution, crime, intoxication, etc.)
For this reason, in principle, producers cannot sell directly to consumers without going through a wholesaler. However, more and more states are allowing direct sales to consumers.
Depending on the severity of the regulations, the states are divided into three categories.
- State direct involvement in alcohol sales
- Control State
- State has a monopoly on one or more of the three tiers
- There are 17 states
- Control State
- No direct state involvement
- Open State
- Little involvement in regulation
- Franchise State
- Franchise laws severely limit changes in Distributors
- Appointment of Distributors is almost always “lifetime” and cannot realistically be changed (because sudden changes in Distributors by Suppliers can be devastating)
- Open State
