The ultimate goal of marketing is to achieve an appropriate level of profit within a set schedule and budget.
もくじ
1. Set marketing goals
Goals may originate from personal intuition, dreams and desires, but what is important is their feasibility.
Marketing goals should be set as specifically as possible, and their feasibility should be clarified through research and analysis.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a framework for analyzing the feasibility of goals.
| Positive Factors | Negative Factors | |
| Internal Factors | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| External Factors | Opportunities | Threats |
Internal Factors:Strengths and Weaknesses
External Factors:Opportunities and Threats
When considering the external business environment, analyze it with PESTEL.
| 分野 | 影響 | 内容 |
|---|---|---|
| Politics | ➖ | Introduce prohibition laws and taxes to curb alcohol consumption. |
| ➕ | Provide subsidies and other promotional support for outstanding products | |
| Economic | ➕ | When the value of a country’s currency declines due to exchange rate fluctuations, the price competitiveness of products increases. |
| ➖ | On the other hand, the cost of purchasing imported equipment and materials will increase. | |
| Social | ➖ | Alcoholic beverages favored by the parents’ generation tend to be avoided. |
| ➖ | Labor shortages are increasing in rural areas. | |
| Technological | ➕ | New production techniques, equipment, and analytical instruments will improve wine quality. |
| ➖ | Improvements in production technology have led to the standardization of wines, resulting in the loss of unique regional styles. | |
| Environmental | ± | Impacts of long-term climate change (can be a threat in areas with established wine styles and an opportunity in cooler areas) |
| Legal | ➕ | Strengthen regional and product branding by establishing strict production regulations, such as France’s AOC. |
| ➖ | At the same time, production regulations limit the options available to producers (e.g. yield limits, restrictions on the grape varieties that can be used, etc.). |
As a result of the analysis of the external environment by PESTEL, a conclusion on the feasibility of the goal is finally drawn.
2. Identification of target products and brands
A product has a life cycle, and the marketing strategy to be achieved depends on the state of the product being targeted.
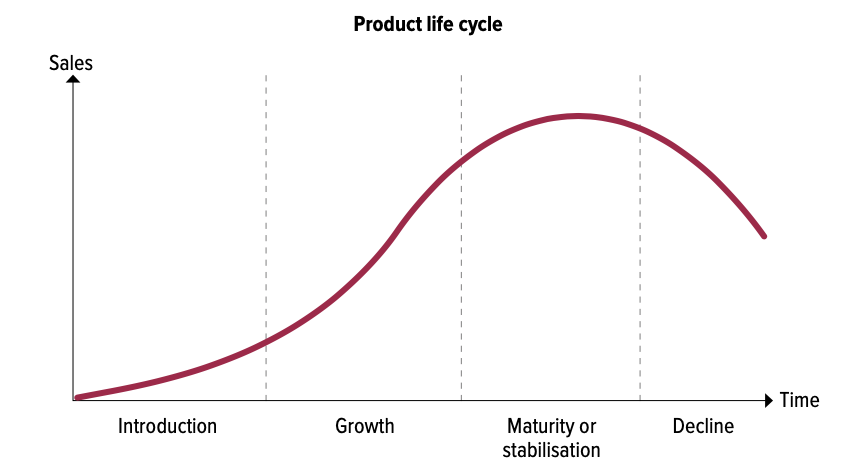
- Introduction:Increase awareness and reputation
- Growth:Spread awareness to a broader target audience to promote strong growth
- Maturity or Stabilisation:Emphasize the differences between the product and other competitive products.
- Decline:Improve products, update packaging, reduce prices, etc. to extend lifecycle
Components of the Brand
| Substance | Consistently provide the same level of quality and style (little variation from vintage to vintage) |
| Consumer Trust | Consistency builds trust in the brand (a key factor in the success of supermarket own label wines). |
| Consumer Engagement | Consumers themselves will maintain a relationship with the brand, seek out the product by name, and spread the word around (slight changes in labels, etc. risk alienating loyal customers). |
| Brand Story | Successful brands have a “story” that consumers can relate to (wine is a product that is relatively easy to tell a story about, and the consumer becomes part of the story). |
| Price Premium | Successful brands are sold at a higher price than other generic products, and the higher price is also seen as a guarantee of quality. |
| Longeviry | Major brands have a long history and will be around for a long time |
| Strong Brand Name | In any language, it is desirable to have a distinctive logo with a name that is easy to remember (names with geographical features and the name of the founder tend to be preferred, and it is important to protect these names through trademark registration) |
| Brand Position | It is advisable to be aware of where your brand is positioned in the market and avoid highly competitive price ranges (although there are opportunities for high volume sales in cheaper markets) |
| Private Label | Having an original label is also important for Supermarkets and Deep Discounters |
There are also the following ways of branding.
- Ladder Brand
- Such as Bourgogne, tiers that are easy for consumers to understand under the same brand
- Accessible:most inexpensive and most frequently purchased(e.g. Bourgogne Rouge)
- Stretch:Affordable, but purchased only on special occasions(e.g. Gevrey-Chambertin)
- Aspiration:Top quality wine that represents the brand and is rarely purchased(e.g. Chambertin)
- Positive Factors
- The finest wines have the effect of throwing their super premium value across the ladder
- Negative Factors
- Not a good match for consumers with low wine knowledge and involvement
- Impressions of inexpensive wines can become impressions of the brand as a whole
- Such as Bourgogne, tiers that are easy for consumers to understand under the same brand
- Soft Brand
- Include information on the label that will help the consumer make a purchase (country of origin, geographical indicators such as region, grape variety, wine style).
- Luxury Brand
- In addition to the quality of the wine itself, promote luxury in every way possible, such as sponsoring luxury events and being on the lists of high-end retailers and restaurants.
3. Identifying Target Markets
It is necessary to identify the consumers that the product is intended for and to know the wants and needs of that target group.
1. Segmentation
Classify the market on a specific axis and divide it into segments.
| Axis of Segment | Examples of Factors |
|---|---|
| Geographical variables | Place of residence (country, region, urban/rural area, etc.) |
| Demographic variables | Age, gender, family structure, income, education level, etc. |
| Psychographic variables | Lifestyle (health-consciousness, liking to eat out, etc.), personality, values and beliefs (vegetarianism, organic orientation), interests, etc. |
| Behavioral variables | ・Benefits sought in wine (cost performance, premium wine, etc.) ・Where, how often, and how much wine is purchased ・Level of interest in wine |
There is no set model for segmentation of wine consumers. One early model is the simple idea of classifying wine consumers into three groups.
- Wine lovers:A person with high income and education who has great interest and in-depth knowledge of wine.
- Wine-interested:A person of moderate or higher education and income who has an interest in wine and possesses a moderate level of knowledge.
- Wine curious:A person with moderate interest in wine but limited knowledge, moderate education and income.
2. Market Research
Market research is about understanding the needs of a particular segment of consumers.
Before conducting market research, it is necessary to clarify the following.
- What information you want to get (e.g., how much a segment is willing to pay for a particular wine)
- Who do you want to collect the information from (a specific segment or general information)?
- How will you conduct the research?
- Secondary Research:Analysis based on publicly available data or reports from market research firms
- Surveys:A method of gathering information from a large number of people through a set of questions
- Focus Groups:Gathering a small group of people and collecting opinions through discussion and comments
- Interviews:A method of eliciting in-depth opinions through one-on-one or small group discussions
- Consumer Behavior Observation:A method of observing and analyzing the behavior of target consumers in actual sales areas.
4. Set Policy for Marketing Strategy
When conducting marketing, you need to decide on a policy based on five axes.
- Direction of marketing strategy
- Mass-oriented (undifferentiated):target is the entire market
- Niche:products aimed at a specific segment, wine is often a niche product
- Multiple:appeal to many segments with one or more products
- Aims of Marketing Strategy
- Aims of Marketing Strategy
- Launch a new product
- Improve existing products
- Increase sales
- Increase market share
- Increase brand awareness
- Attract new consumers, etc.
- Target values to be achieved(profit, sales amount, sales volume, market share, etc.)
- Time frame for achieving the target
- Marketing budget
5. Marketing Strategy Planning
When planning a specific marketing strategy, each element is examined in terms of the 5Ps. (Process and Physical Evidence are not discussed here because they are elements of services.)
- Product:製品
- Price:価格
- People / Person:人
- Place:場所
- Promotion:販売促進
① Product:製品
Product is the wine itself, including the packaging and branding.
Since the wine market is often described as “saturated,” you need to clearly explain how your product is different from your competitors’ products.
Therefore, the presentation of the product – the bottle, label, and other packaging – needs to be designed to appeal to the target consumer.
② Price:価格
Price is the total amount that a consumer pays for a product, including shipping and other costs.
It also includes the cost of time and effort that the consumer spends to purchase the wine.
Price has a strong influence on consumers when they make purchase decisions. Therefore, the “penetration strategy” of setting a lower price than similar products of other companies and rapidly spreading the product in the market is effective. However, it is not easy to get people to continuously purchase a product when the price of the product is raised.
③ People / Person:人
There are two interpretations of “person,” and both are important.
- Target
- Characteristics and behaviors of target consumers
- Staff, partners and customers
- Cellar Door and Event Sales: Hire and train staff who have sufficient knowledge and can provide appropriate services to customers.
- Retail sales: It is important to share the image and vision of the producer with distributors and retailers (brochures, videos, website development, etc.)
④ Place:場所
The location where wine is sold depends on the target consumer.
| Consumers’ interest in wine | Where to Buy | Wines to Seek |
|---|---|---|
| High | ・Specialist Wine Retailers ・Premium Supermarkets ・Deep Discounters | ・Premium wines ・Lesser-known regions and grape varieties |
| Low | ・Supermarkets | ・Inexpensive to mid-priced wines ・Well-known regions and grape varieties |
The wines to be sold and the distribution channels will also vary depending on the maturity of the wine market in a country or region.
| Market Maturity | Status | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Mature | Markets where wine appears to have reached its potential with stable or declining volumes. | Germany, France, UK |
| Established | Markets with strong historical growth that is tailing off. | Italy, South Africa |
| Growth | Markets where wine is a mainstream product and/or experiencing growth. | USA, Canada, Brazil |
| Emerging | Markets where wine is experiencing growth and shows potential from a relatively low base. | China, Russia, Turkey |
| New Emerging | Markets where wine is still a relatively new and unknown beverage, but showing some potential. | India, Malaysia, Philippines |
⑤ Promotion:販売促進
There are two types of promotion: one is do when the wine is sale, and the other is do outside the time of sale, such as advertising.
All of these promotions related to alcohol sales are regulated by each country, so care must be taken when implementing them.
1. Promotion at the Point of Sale
| # | Promotion | Features | Mass Production | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Price Promotion 価格訴求 | ➕ Price reduction is a common promotion because price has a great influence on consumers’ purchase decisions. ➖ However, it should be done with caution because of the risk of damaging the image of the product or failing to increase customer loyalty. | ◎ | × |
| 2 | Competitions 懸賞 | ➕ It can encourage the purchase of specific products. ➕ Contact information and other information can be obtained by entering a sweepstakes, and can be used for ongoing promotion. | ◯ | × |
| 3 | Limited Edition Packaging 限定版パッケージ | ➕ It will improve the image of the brand ➖ Does not improve sales in the long term | ◯ | ◯ |
| 4 | Consumer Tastings テイスティング | ➕ Offering a tasting may increase sales. ➕ It will be more likely to purchase the wine in the future. | × | × |
| 5 | Staff Incentives インセンティブ付与 | ➕ May increase sales by motivating staff to sell more ※ Illegal in China (considered bribery and unfair competition) | ◯ | × |
| 6 | Staff Training トレーニング | ➕ Staff members are encouraged to sell the products themselves and with enthusiasm, which can lead to increased sales. | × | ◯ |
Examples for Price Promotion
In many markets, retailers periodically run some kind of price promotion, the purpose of which is to
- Expansion of sales of existing products
- Mass sales and recognition expansion of new products
- Acquisition of new customers
- To replace products (sell off old stock or discontinued products)
The actual price promotion can be done in the following ways.
| # | Promotion | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Discounts on specific product | ・Stock clearance of specific products |
| 2 | Discounts on specific days or seasons | ・Sales promotion on weekdays when the market is quiet ・Sales promotion during Christmas, etc. |
| 3 | Discounts for specific groups | ・Students, military personnel, etc. |
| 4 | Multi-buy / Volume Discounts | ・BOGOF(Buy One Get One Free) ※Banned in some countries such as Sweden and Scotland because it is believed to encourage excessive alcohol consumption |
| 5 | Link-saves リンクセーブ | ・A method of offering a discount on another category of products for the purchase of a certain product or an order of a certain quantity. e.g., discounts on food when a certain wine is ordered, free delivery when six or more bottles are ordered, etc. |
2. Promotion Away from the point of Sale
| # | Promotion | Features | Mass-Production | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Advertising 広告 | ➕ Very powerful tool to promote products to a large and wide range of consumers ➖ Can be very expensive, although it depends on the channel (press ads for wine and food are suitable) | ◎ | ○ |
| 2 | Social Media | ℹ️ Unlike traditional advertising, it is important to interact with consumers (using it only for advertising tends to keep followers away) ± Everyone can easily share their experiences with others. ± Peer reviews are becoming increasingly important in wine buying decisions. ➖ Can lead to negative publicity and reviews | ◎ | × |
| 3 | Web Site & Smartphone Apps | ℹ️ It is essential to create and maintain a website that is attractive and easy to navigate. ℹ️ SEO measures are necessary to ensure that the site appears at the top of search results. ➕ Producers can communicate with a large number of people around the world. ➖ Hiring consultants and IT experts can be costly | ◎ | ◎ |
| 4 | Reviews & Awards レビューと受賞 | ➕ Favorable reviews and high scores by reputable critics can greatly increase wine sales. ➕ Awards and medals can be used in promotional materials and sales. ➕ Greatly influence purchase decisions, especially for less engaged and knowledgeable consumers. ➖ There is a cost associated with participating in competitions and providing bottles of wine (but many producers consider it a worthwhile expense) | ◯ | ◯ |
| 5 | Public Relations PR | ℹ️ The purpose of PR is to create a positive image of the company among consumers ℹ️ Brand ambassadors are one of the successful methods (in China, the appointment of key opinion leaders has been successful) ➕ Social and corporate responsibility policies create a positive image for many consumers. | ◯ | △ |
| 6 | Sponsorship スポンサー | ℹ️ Many sporting and cultural events are financially supported by sponsorship deals. ➕ Branding and advertising can be effective if the target audience is aligned. ➖ The appropriateness of linking health promotion activities with alcohol has been questioned, especially in the sports sector. | ◯ | × |
| 7 | Wine Tourism ワインツーリズム | ℹ️ Some wineries offer hands-on events that allow visitors to participate in harvesting and brewing. ℹ️ Successful wine tourism involving not only wine producers, but also tour operators, restaurants, hotels, and other local tourism businesses. ➕ More opportunities for interaction with general consumers ➕ People who visit producers generally become regular customers and are likely to recommend their wines to others. ➖ High cost of infrastructure and high cost of operation and maintenance | × | ◯ |
| 8 | Events & Festivals イベント・フェスタ | ➕ Attracts a wide range of consumers and provides an opportunity to attract new customers. ➖ Costs such as exhibition fees, travel expenses for booth management, and staff costs will be incurred. ➖ Depending on how the event is managed, it may turn into an all-you-can-drink event instead of a tasting. | ◯ | × |
| 9 | Free Merchandise 無料商品 | ℹ️ Provide wine goods and other promotional goods that are not directly related ➕ Increasing consumer loyalty will lead to future wine sales. ➕ Increasing brand awareness among the people around you, leading to indirect sales promotion. | ◯ | × |
Types and characteristics of advertisements
| # | Types of Ads | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TV, Cinema | ➕ The most powerful advertising campaign and can appeal to a large number of people ➖ Very expensive |
| 2 | Radio | ➕ Advertising with a low marketing budget is possible. ➖ Difficult to leave a lasting impression due to the lack of images |
| 3 | Press Advertising | ℹ️ It is important to place ads in the right media. ℹ️ Some techniques increase effectiveness by having well-known writers write articles (advertorials). ➕ Very effective in telling a detailed story ➕ Low cost |
| 4 | Billboards | ➖ Billboard advertising has a limited effect because most people only see it for a short time. |
| 5 | Digital Advertising | ➕ Since the number of advertisements published is linked to the advertising cost, it is easy to measure the effectiveness. ➕ Marketing can be done at a relatively low cost. |
6. Implement and Monitor Marketing Strategies
After planning the strategy, the actual marketing should be conducted and monitored to see if the targeted results are being obtained.
If the targeted results are not being achieved, a decision needs to be made to change the strategy or goals, stop the marketing, or eventually stop selling the product.
There are two ways to measure the effectiveness of marketing: monitoring of targeted figures and surveys to ascertain consumer response. This is called “marketing research”.
- Create focus groups and ask for direct feedback
- Eye tracking
- Viral marketing research
